中文名稱: 兔抗ACY1多克隆抗體
|
Background: |
This gene encodes a cytosolic, homodimeric, zinc-binding enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of acylated L-amino acids to L-amino acids and an acyl group, and has been postulated to function in the catabolism and salvage of acylated amino acids. This gene is located on chromosome 3p21.1, a region reduced to homozygosity in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), and its expression has been reported to be reduced or undetectable in SCLC cell lines and tumors. The amino acid sequence of human aminoacylase-1 is highly homologous to the porcine counterpart, and this enzyme is the first member of a new family of zinc-binding enzymes. Mutations in this gene cause aminoacylase-1 deficiency, a metabolic disorder characterized by central nervous system defects and increased urinary excretion of N-acetylated amino acids. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the upstream ABHD14A (abhydrolase domain containing 14A) gene, as represented in GeneID:100526760. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 18. |
|
Applications: |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
|
Name of antibody: |
ACY1 |
|
Immunogen: |
Fusion protein of human ACY1 |
|
Full name: |
aminoacylase 1 |
|
Synonyms: |
ACY-1; ACY1D |
|
SwissProt: |
Q03154 |
|
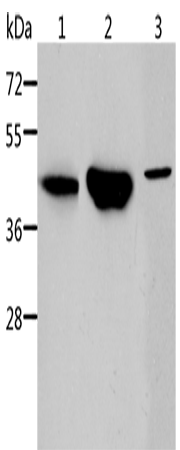
IHC positive control: |
Human gastric cancer and human colon cancer |
|
IHC Recommend dilution: |
25-100 |
|
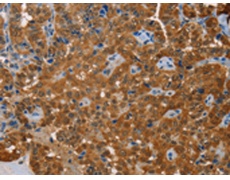
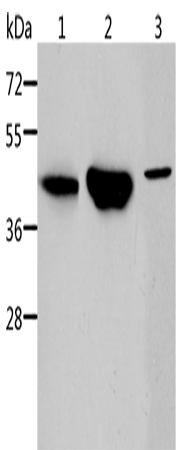
WB Predicted band size: |
46 kDa |
|
WB Positive control: |
Mouse kidney and human normal kidney tissue, K562 cells |
|
WB Recommended dilution: |
200-1000 |
 購物車
購物車 幫助
幫助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009