反應(yīng)種屬: Human
克隆類型: rabbit polyclonal
技術(shù)規(guī)格
Background:
Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) are a group of enzymes closely related to sirtuins. They catalyze the removal of acetyl groups from lysine residues in histones and non-histone proteins, resulting in transcriptional repression. In general,they do not act autonomously but as components of large multiprotein complexes, such as pRb-E2F and mSin3A, that mediate important transcription regulatory pathways. There are three classes of HDACs; classes 1, 2 and 4, which are closely related Zn2+-dependent enzymes. HDACs are ubiquitously expressed and they can exist in the nucleus or cytosol. Their subcellular localization is effected by protein-protein interactions (for example HDAC-14.3.3 complexes are retained in the cytosol) and by the class to which they belong (class 1 HDACs are predominantly nuclear whilst class 2 HDACs shuttle between the nucleus and cytosol). HDACs have a role in cell growth arrest, differentiation and death and this has led to substantial interest in HDAC inhibitors as possible antineoplastic agents.
Applications:
WB, IHC
Name of antibody:
HDAC4/HDAC5/HDAC9 (phospho-Ser246/259/220)
Immunogen:
Synthetic peptide of human HDAC4/HDAC5/HDAC9 (phospho-Ser246/259/220)
Full name:
HDAC4/HDAC5/HDAC9 (phospho-Ser246/259/220)
Synonyms:
HD4/HD5/HD9
SwissProt:
P56524/Q9UQL6/Q9UKV0
IHC positive control:
Human breast carcinoma
IHC Recommend dilution:
50-100
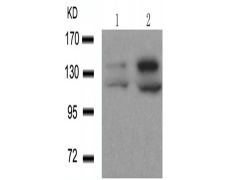
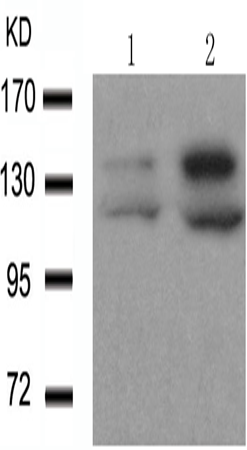
WB Predicted band size:
124 kDa; 140 kDa
WB Positive control:
293 cells untreated or treated with EGF
WB Recommended dilution:
500-1000



 購物車
購物車 幫助
幫助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009