中文名稱: 兔抗COX4I2多克隆抗體
|
Background: |
Cytochrome c oxidase (COX), the terminal enzyme of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, catalyzes the electron transfer from reduced cytochrome c to oxygen. It is a heteromeric complex consisting of 3 catalytic subunits encoded by mitochondrial genes and multiple structural subunits encoded by nuclear genes. The mitochondrially-encoded subunits function in electron transfer, and the nuclear-encoded subunits may be involved in the regulation and assembly of the complex. This nuclear gene encodes isoform 2 of subunit IV. Isoform 1 of subunit IV is encoded by a different gene, however, the two genes show a similar structural organization. Subunit IV is the largest nuclear encoded subunit which plays a pivotal role in COX regulation. |
|
Applications: |
ELISA, IHC |
|
Name of antibody: |
COX4I2 |
|
Immunogen: |
Synthetic peptide of human COX4I2 |
|
Full name: |
cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4I2 |
|
Synonyms: |
COX4; COX4B; COX4-2; COX4L2; COXIV-2; dJ857M17.2 |
|
SwissProt: |
Q96KJ9 |
|
ELISA Recommended dilution: |
5000-10000 |
|
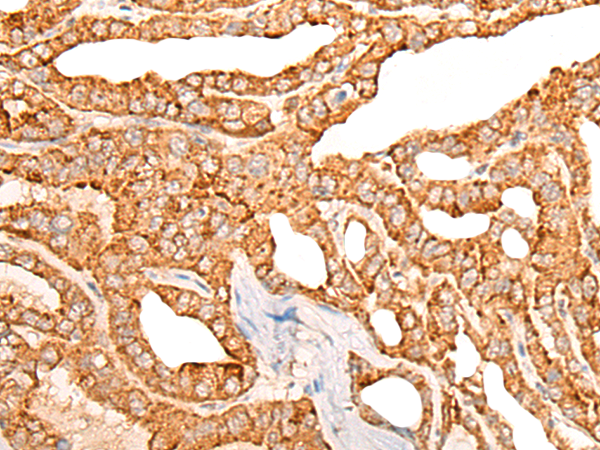
IHC positive control: |
Human thyroid cancer |
|
IHC Recommend dilution: |
25-100 |

 購物車
購物車 幫助
幫助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009