|
Background: |
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed by natural killer cells and subsets of T cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic and highly homologous and they are found in a cluster on chromosome 19q13.4 within the 1 Mb leukocyte receptor complex (LRC). The gene content of the KIR gene cluster varies among haplotypes, although several "framework" genes are found in all haplotypes (KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR3DL4, KIR3DL2). The KIR proteins are classified by the number of extracellular immunoglobulin domains (2D or 3D) and by whether they have a long (L) or short (S) cytoplasmic domain. |
|
Applications: |
ELISA, IHC |
|
Name of antibody: |
KIR2DL3/KIR2DL1/KIR2DL4/KIR2DS4 |
|
Immunogen: |
Fusion protein of human KIR2DL3/1/4/S4 |
|
Full name: |
killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, two domains, long cytoplasmic tail, 3/1/4/ short cytoplasmic tail, 4 |
|
Synonyms: |
p58; NKAT; GL183; NKAT2; CD158b; NKAT2A; NKAT2B; CD158B2; KIR-K7b; KIR-K7c; KIRCL23; KIR-023GB/NKAT; NKAT1; p58.1; CD158A; KIR221; KIR-K64/ G9P; CD158D; KIR103; KIR103AS/ KKA3; KIR1D; NKAT8; CD158I; KIR412 |
|
SwissProt: |
P43628/P43626/Q99706/P43632 |
|
ELISA Recommended dilution: |
1000-2000 |
|
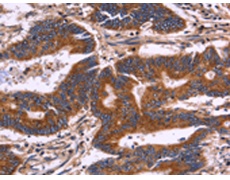
IHC positive control: |
Human colon cancer and human thyroid cancer |
|
IHC Recommend dilution: |
50-100 |

 購(gòu)物車
購(gòu)物車 幫助
幫助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009